Exercises 2 - Objects Solutions
2.1 Creating R Objects
- The code below creates a vector of three character strings (more on
vectors shortly). Use this code and the ‘storage arrow’ to create an
object names
adj.
c("scary","intelligent","new")
Solution:
adj <- c("scary","intelligent","new")
adj
## [1] "scary" "intelligent" "new"
- Similarly, create an object called
nounsusing the storage arrow and code below.
c("bugs", "beings", "houses")
Solution:
nouns <- c("bugs", "beings", "houses")
nouns
## [1] "bugs" "beings" "houses"
- The
paste()function is useful for combining character strings. After completing the above parts, run the following:
paste(adj, nouns)
## [1] "scary bugs" "intelligent beings" "new houses"
2.2 Investigating Objects
irisis a built-in R object (that means you have it in your environment even if it doesn’t show it). Determine theclassand structure (str) of theirisobject.
Solution:
class(iris)
## [1] "data.frame"
str(iris)
## 'data.frame': 150 obs. of 5 variables:
## $ Sepal.Length: num 5.1 4.9 4.7 4.6 5 5.4 4.6 5 4.4 4.9 ...
## $ Sepal.Width : num 3.5 3 3.2 3.1 3.6 3.9 3.4 3.4 2.9 3.1 ...
## $ Petal.Length: num 1.4 1.4 1.3 1.5 1.4 1.7 1.4 1.5 1.4 1.5 ...
## $ Petal.Width : num 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.2 0.1 ...
## $ Species : Factor w/ 3 levels "setosa","versicolor",..: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
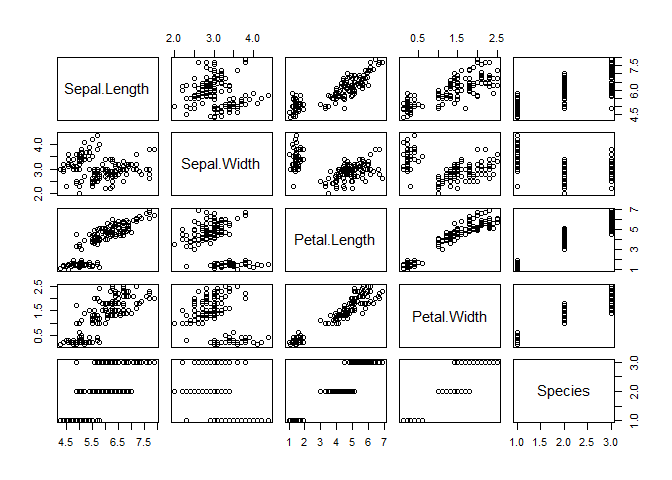
- Run the code below to create a quick visual of this dataset. Note
that R is determining what to do with the
plot()function based on the object given to it!
plot(iris)